How to use the full chemical name of a dye to deduce its molecular structure and other information
Name: Fatma
—ADVERTISEMENTS—
Books about the chemistry of dyeingExtremely useful for understanding many aspects of different classes of dyes.
May be ordered directly from the AATCC (The American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists) or

Wool Dyeing
Edited by David M. Lewis, 1992.
Vinyl sulfone dyes work well on wool. Highly technical and thorough, this book explains all aspects of wool dyeing in a manner understandable by textile professionals and advanced science students.
Victor B. Ivanov's

Reactive Dyes in Biology and Medicine
Explains use of reactive dyes for staining proteins or carbohydrates
Waring and Hallas's

The Chemistry and Application of Dyes (Topics in Applied Chemistry)
includes recipes for synthesizing reactive dyes
Heinrich Zollinger
Color Chemistry: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications of Organic Dyes and Pigments
John Shore's

Cellulosies Dyeing
Vinyl sulfone dyes are much used commercially for the dyeing of cellulosic fabrics. This book includes useful information about the chemistry of reactive dyes, and other dye types used for cotton and other plant fibers
Country or region: Turkey
Message: Hello, first of all thanks for this web page... in my thesis I am working with removing dye (Remazol Yellow RR) with S. cereviaie. I want to ask you the molecular formula of this dye and also other information about it... thanks a lot....
Your Remazol Yellow RR is not listed on my chart of Remazol dyes with their generic names and sources. (See my page, "Vinyl Sulfone Fiber Reactive Dyes".) It does not appear to have a Colour Index name, either, at least as of the most recent information I find on it in a quick search, though what I do find dates from a full decade ago. Sometimes a search with a chemical's CAS number in quotes, in this case "189574-45-6", turns up more information, but that doesn't seem to get us any farther in this case.
You undoubtedly already have the 2007 Demir article [PDF] about decolorization of this dye by a white rot fungus, in which the following properties are given:
Structure: Granule
Color: Deep yellow
Odor: Odorless
Melting point: >200°C
Density: 0,48 g/cm3
Aqueous solubility: 100 gl-1 (20°C)
pH: 5-6 (10 gl-1, 20°C)
Flash point: Not determined
Kindling point: >300°C
Color: Deep yellow
Odor: Odorless
Melting point: >200°C
Density: 0,48 g/cm3
Aqueous solubility: 100 gl-1 (20°C)
pH: 5-6 (10 gl-1, 20°C)
Flash point: Not determined
Kindling point: >300°C
Not much of that is very useful, though, and the density is likely to vary from one batch of the dye powder to another. You should also have the Material Safety Data Sheet from Dystar which was the original source of this information. Various online US tariff documents, however, reveal the full chemical name:
Benzenesulfonic acid, 2-amino-4-(cyanoamino)-6-[(3-sulfophenyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl]amino]-5-[[4-[[2-(sulfoxy)ethyl]sulfonyl]phenyl]azo]-, lithium sodium salt (CAS No. 189574–45–6) ["Remazol Yellow RR Gran"] (source [XLS])
With this name you can figure out how to draw the chemical structure, you can add up the atoms to get the molecular formula, and you can learn a little more about the dye's properties. Unfortunately, the name as given is not quite correct: there are more closing parentheses than opening parentheses, which is confusing. It's good enough to work with, however.
The full chemical names of dyes can be difficult to follow at first, because it's not immediately obvious what parts go where. The secret is to start with the basic dye structure, and figure out where, on that basic form, the numbering indicates that the various sections of the dye molecule should go. Break up the name given above as follows:
Benzenesulfonic acid,
2-amino-
4-(cyanoamino)-
6-[(3-sulfophenyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl]amino]-
5-[[4-[[2-(sulfoxy)ethyl]sulfonyl]phenyl]azo]-, lithium sodium salt.
The structure of Remazol Yellow RR is based on benzenesulfonic acid. Benzenesulfonic acid is the following structure:
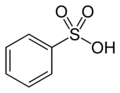
(from Wikipedia). Start by determining which atom, on the benzenesulfonic acid molecule, has which number. Atom number 1 in the benzene ring is the one that has the sulfonic acid on it. Starting in either direction, atom 2 is the one next to it, and so on.
The name indicates that atom number 2 has an amino group, -NH2, on it.
Next, on atom number 4, opposite the sulfonic acid group, is a cyanoamino group, -NH-C≡N. (That's a triple bond between the C and the last N.)
On atom number 5 is [[4-[[2-(sulfooxy) ethyl]sulfonyl] phenyl]azo]-, which contains a beta-sulfatoethylsulfone that is what produces the vinyl sulfone reactive group; it is attached to the benzenesulfonic acid through an azo-bonded phenyl group. The beta-sulfatoethylsulfone is the section that causes the dye to be classed among the Remazol (vinyl sulfone) dyes, and allows it to form a covalent molecular bond to cellulose- and protein-based textile fibers. The vinyl sulfone group itself, -SO2-CH=CH2, is masked on the end with a sulfato group that is be eliminated before the dye reacts with the textile fiber molecule.
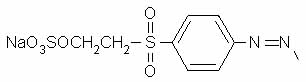
The azo bond, in which two nitrogens are connected to each other by a double bond, is often seen among synthetic dyes, as it is one of the most useful sources of color, especially common among yellows and reds. One frequently hears general statements about the hazards of azo dyes, but in fact it's only a limited subset of azo dyes that are considered dangerous for use. Azo dyes can undergo reductive cleavage at the azo bond to form two amines; the azo dyes banned in Europe are those in which one of the two resulting amines is on a list of 22 known or suspected carcinogens, such as benzidine and 4-chloroaniline. Reductive decolorizing of these dyes occurs at the same time as and by the same process by which a hazardous aromatic amine is regenerated, so decolorizing is not itself a sign that all potentially toxic chemicals have been destroyed.
On atom number 6 is [(3-sulfo phenyl)amino]- 1,3,5-triazin- 2-yl]amino]. Triazine structures are commonly used in reactive dyes; halogen-substituted triazines are particularly useful in forming reactive structures in dye molecules, but that's not what the triazine is being used for in this case. The sulfonate on the end adds to the dye's water-solubility, and presumably this section as a whole does affect the overall color of the molecule.
You can connect the different parts together to give a structure like this:
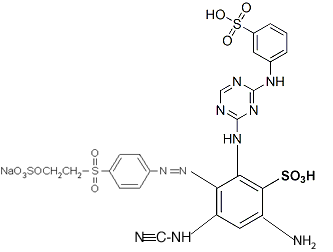
....though clearly it needs to be redrawn, not forgetting the lithium ion, which was inadvertently omitted in this drawing (instead there is an extra hydrogen in place of it on one of the sulfonates). If you use this structure for anything, you should get someone else to double-check it, in order to be certain I've done it correctly; it's been many years since I did much chemistry (my last degree was in biology).
Compare to other Remazol dyes whose names and structures are both readily available. Here is Remazol yellow 4R, Colour Index reactive yellow 14, whose IUPAC name is sodium 3-chloro-4-[4-[2-methoxy-5-(2-sulfonatooxyethylsulfonyl)phenyl]diazenyl-3-methyl-5-oxo-4H-pyrazol-1-yl]-5-methylbenzenesulfonate:
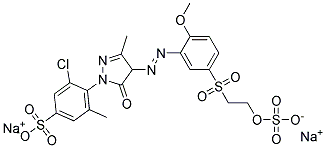
(from http://www.lookchem.com/REMAZOL-YELLOW-G/)
And compare to Remazol Orange 3R, Colour Index reactive orange 16, whose full name is 2-Naphthalenesulfonic acid, 6-(acetylamino)- 4-hydroxy- 3-((4-((2-(sulfooxy)ethyl) sulfonyl)phenyl)azo)-, disodium salt:
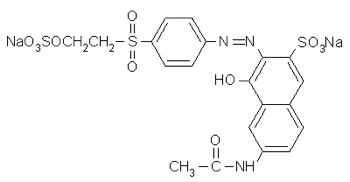
With practice you can gather quite a lot of information from the full chemical name of a dye.
(Please help support this web site. Thank you.)
(Please help support this web site. Thank you.)
Posted: Wednesday - May 16, 2012 at 08:45 AM
Follow this blog on twitter here.
Quick Links
- All About Dyes & Dyeing Top -
- Top of this blog -
- FAQ -
- The Dye Forum -
- How to Tie Dye - How to Batik -
- Books - Toys - Plants -
- Top of this blog -
- FAQ -
- The Dye Forum -
- How to Tie Dye - How to Batik -
- Books - Toys - Plants -
More in this category:
- -
Statistics
Total entries in this blog:
Total entries in this category:
Published On: Aug 29, 2012 02:49 PM
Total entries in this category:
Published On: Aug 29, 2012 02:49 PM

